Pages
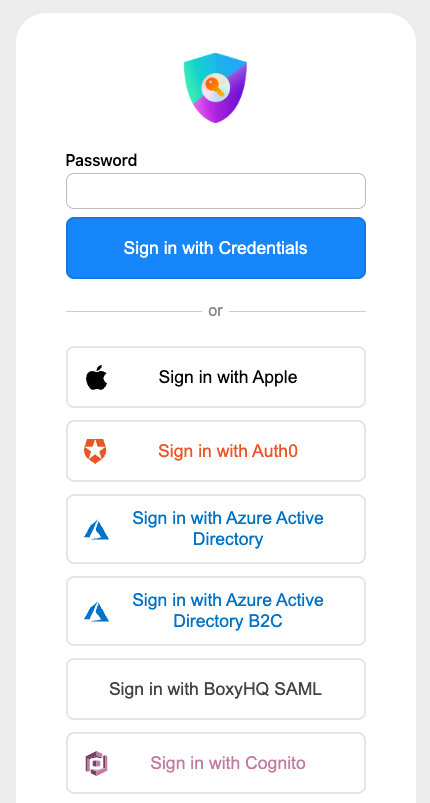
Auth.js automatically creates simple, unbranded authentication pages for handling Sign in, Sign out, Email Verification and displaying error messages.
The options displayed on the sign-up page are automatically generated based on the providers specified in the options passed to Auth.js.
To add a custom login page, you can use the pages option:
...
pages: {
signIn: '/auth/signin',
signOut: '/auth/signout',
error: '/auth/error', // Error code passed in query string as ?error=
verifyRequest: '/auth/verify-request', // (used for check email message)
newUser: '/auth/new-user' // New users will be directed here on first sign in (leave the property out if not of interest)
}
...
When using this configuration, ensure that these pages actually exist. For example error: '/auth/error' refers to a page file at pages/auth/error.js.
Error codes
We purposefully restrict the returned error codes for increased security.
Error page
The following errors are passed as error query parameters to the default or overridden error page:
- Configuration: There is a problem with the server configuration. Check if your options are correct.
- AccessDenied: Usually occurs, when you restricted access through the
signIncallback, orredirectcallback - Verification: Related to the Email provider. The token has expired or has already been used
- Default: Catch all, will apply, if none of the above matched
Example: /auth/error?error=Configuration
Sign-in page
The following errors are passed as error query parameters to the default or overridden sign-in page:
- OAuthSignin: Error in constructing an authorization URL (1, 2, 3),
- OAuthCallback: Error in handling the response (1, 2, 3) from an OAuth provider.
- OAuthCreateAccount: Could not create OAuth provider user in the database.
- EmailCreateAccount: Could not create email provider user in the database.
- Callback: Error in the OAuth callback handler route
- OAuthAccountNotLinked: If the email on the account is already linked, but not with this OAuth account
- EmailSignin: Sending the e-mail with the verification token failed
- CredentialsSignin: The
authorizecallback returnednullin the Credentials provider. We don't recommend providing information about which part of the credentials were wrong, as it might be abused by malicious hackers. - SessionRequired: The content of this page requires you to be signed in at all times. See useSession for configuration.
- Default: Catch all, will apply, if none of the above matched
Example: /auth/signin?error=Default
Theming
By default, the built-in pages will follow the system theme, utilizing the prefer-color-scheme Media Query. You can override this to always use a dark or light theme, through the theme.colorScheme option.
In addition, you can define the background color and text color of the button with the theme.brandColor and theme.buttonText options. You can also define a URL to a logo in theme.logo which will be rendered at the top of the card.
Sign In
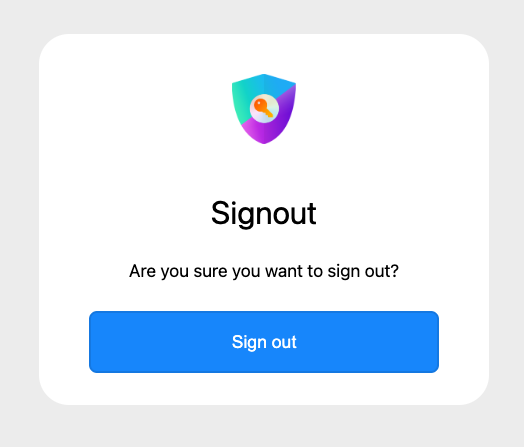
Sign Out
Examples
OAuth Sign in
In order to get the available authentication providers and the URLs to use for them, you can make a request to the API endpoint /api/auth/providers:
import { getProviders, signIn } from "next-auth/react"
export default function SignIn({ providers }) {
return (
<>
{Object.values(providers).map((provider) => (
<div key={provider.name}>
<button onClick={() => signIn(provider.id)}>
Sign in with {provider.name}
</button>
</div>
))}
</>
)
}
export async function getServerSideProps(context) {
const providers = await getProviders()
return {
props: { providers },
}
}
There is another, more fully styled example signin page available here.
Email Sign in
If you create a custom sign in form for email sign in, you will need to submit both fields for the email address and csrfToken from /api/auth/csrf in a POST request to /api/auth/signin/email.
import { getCsrfToken } from "next-auth/react"
export default function SignIn({ csrfToken }) {
return (
<form method="post" action="/api/auth/signin/email">
<input name="csrfToken" type="hidden" defaultValue={csrfToken} />
<label>
Email address
<input type="email" id="email" name="email" />
</label>
<button type="submit">Sign in with Email</button>
</form>
)
}
export async function getServerSideProps(context) {
const csrfToken = await getCsrfToken(context)
return {
props: { csrfToken },
}
}
You can also use the signIn() function which will handle obtaining the CSRF token for you:
signIn("email", { email: "jsmith@example.com" })
Credentials Sign in
If you create a sign in form for credentials based authentication, you will need to pass a csrfToken from /api/auth/csrf in a POST request to /api/auth/callback/credentials.
import { getCsrfToken } from "next-auth/react"
export default function SignIn({ csrfToken }) {
return (
<form method="post" action="/api/auth/callback/credentials">
<input name="csrfToken" type="hidden" defaultValue={csrfToken} />
<label>
Username
<input name="username" type="text" />
</label>
<label>
Password
<input name="password" type="password" />
</label>
<button type="submit">Sign in</button>
</form>
)
}
export async function getServerSideProps(context) {
return {
props: {
csrfToken: await getCsrfToken(context),
},
}
}
You can also use the signIn() function which will handle obtaining the CSRF token for you:
signIn("credentials", { username: "jsmith", password: "1234" })
Remember to put any custom pages in a folder outside /pages/api which is reserved for API code. As per the examples above, a location convention suggestion is pages/auth/....